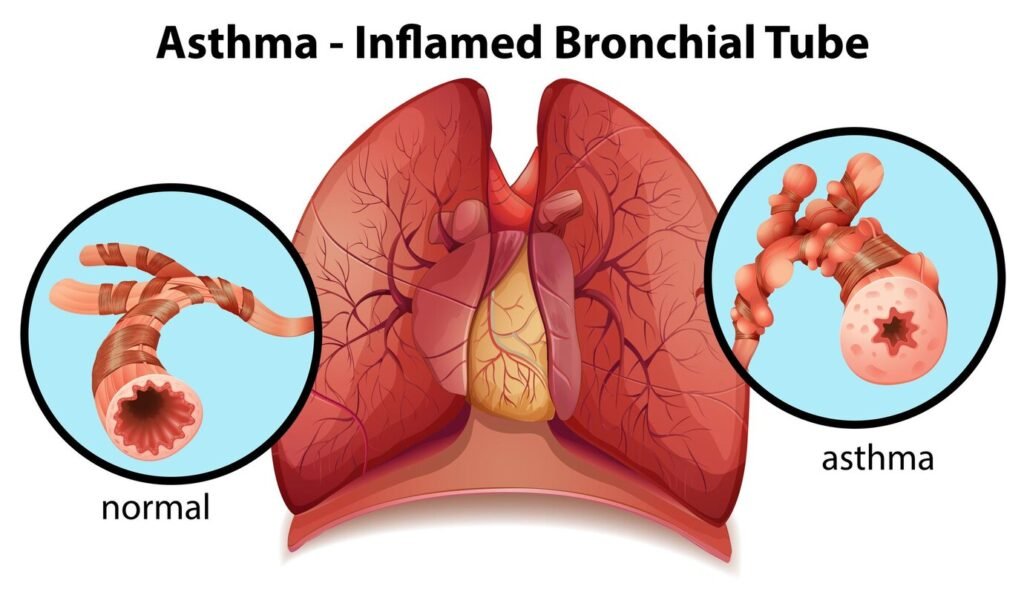
Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease that affects people of all ages. It is characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, which can make it difficult to breathe and trigger coughing, wheezing, and chest tightness. Asthma attacks can be triggered by a variety of factors, including allergens, exercise, cold air, and smoke. While there is no cure for asthma, it can be managed with medication and lifestyle changes.
Asthma is one of the most common respiratory system diseases in the world. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), asthma affects an estimated 262 million people worldwide and is responsible for 455,000 deaths each year. Asthma is more common in children than in adults, and it is more common in males than in females.
In this article, we will discuss the definition, risk factors, and causes of asthma. We will also provide information on how asthma is diagnosed and treated. Finally, we will offer some tips on how to manage asthma and live a healthy life.
What is Asthma?
Asthma is a lung condition that makes it difficult for sufferers to breathe due to inflammation and narrowing of the airways.
In addition to breathing difficulties, asthma also causes other symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, and chest pain.
The airways in people with asthma are more sensitive compared to those without asthma.
When the lungs are irritated by triggers (such as cigarette smoke, dust, animal fur, etc.), the muscles around the airways become stiff and narrow.
Asthma Symptoms
A person with asthma can experience various symptoms, such as:
- Chest tightness;
- Coughing, especially at night or early morning;
- Shortness of breath;
- Wheezing, which produces a whistling sound when exhaling.
The pattern of symptoms in each person with asthma can vary. However, the most common symptom patterns include:
- Coming and going over time or within the same day;
- Starting or worsening with a viral infection, like a cold;
- Triggered by exercise, allergies, cold air, or hyperventilation due to laughing or crying;
- Worse at night or in the early morning.
Asthma Risk Factors
Bacteria from dust often become the main trigger for asthma.
These bacteria, called endotoxins, are typically found in household items, especially in the bedroom, and can cause asthma symptoms.
Other risk factors that can trigger asthma include:
- Cigarette smoke.
- Animal fur.
- Cold air.
- Viral infections.
- Exposure to chemicals.
- Physical activity.
- Infections of the lungs and upper respiratory tract.
- Certain occupations such as welders, carpenters, or textile factory workers.
- Excessive emotions (hysterical laughter or prolonged sadness).
- Food allergies, such as nuts.
Causes of Asthma
Asthma is a condition that can affect people of all ages.
It is most often caused by dust, cigarette smoke, animal fur, cold air, physical activity, viral infections, and chemical exposure.
However, the primary cause of asthma is still not definitively known. Nonetheless, it is proven that people with asthma have more sensitive airways.
When the lungs are irritated, the muscles around the airways become stiff and narrow. Then, mucus production increases, making it difficult for sufferers to breathe.
In children, asthma symptoms often disappear on their own as they reach adolescence.
However, children with severe asthma symptoms may have the condition persist or recur later in life.
Asthma Diagnosis
Initially, the doctor will conduct a medical interview (anamnesis) and a physical examination.
It’s important to note that the diagnosis of asthma is based on episodic symptoms such as coughing, shortness of breath, wheezing, chest tightness, and variability related to weather conditions.
To help confirm the diagnosis of asthma, the doctor may need to perform several supporting tests.
For example, lung function tests using a spirometer. Lung function measurements are used to assess:
- Airway obstruction;
- Reversibility of lung function abnormalities;
- Variability in lung function, as an indirect assessment of airway hyper-responsiveness.
There are also several other tests to help the doctor diagnose asthma, including:
- Peak expiratory flow measurement with a peak flow rate meter;
- Reversibility test (with bronchodilators);
- Bronchial provocation test, to assess the presence of bronchial hyperactivity;
- Allergy tests to determine the presence of allergies;
- Chest X-ray, to rule out diseases other than asthma.
Asthma Complications
Untreated asthma can lead to various complications, such as:
- Psychological issues (anxiety, stress, or depression);
- Decreased performance at school or work;
- Frequent fatigue;
- Growth and puberty disorders in children;
- Status asthmaticus, a severe asthma condition that does not respond to standard therapy;
- Pneumonia;
- Respiratory failure;
- Damage to part or all of the lungs;
- Death.
What Should You Do to Treat Asthma?
In treating asthma, there are two main objectives: relieving symptoms and preventing recurrence. Therefore, it is important to seek treatment from a doctor who can prescribe medication to manage asthma.
In addition to treatment, asthma sufferers must also avoid triggers that can cause asthma to flare up. Doctors usually recommend an inhaler as a treatment when asthma symptoms appear. However, using an inhaler can also cause side effects.
1. Mild Inhaler Side Effects:
- Dizziness accompanied by headaches
- Insomnia or difficulty sleeping
- Muscle pain
- Nasal congestion and runny nose
- Dryness in the mouth and throat
- Coughing even when not sick
- Sore throat leading to hoarseness
2. Severe Side Effects to Watch For:
Contact a doctor immediately if you experience any of the following side effects:
- Chest pain, irregular heartbeats
- Hand tremors
- Symptoms of anxiety
- High blood pressure
- Decreased potassium levels in the blood, which can lead to extreme thirst, muscle weakness, and fatigue
- Difficulty breathing
3. Side Effects of Steroid Hormone Inhalers:
- Mouth pain
- Fungal infections in the mouth
- Weakening of bones in adults
- Development of glaucoma or increased eye pressure, particularly with long-term use
If an asthma attack occurs with worsening symptoms despite using an inhaler or medication, medical intervention at a hospital is necessary because asthma can be life-threatening.
Prevention is Better than Cure
Asthma can be controlled by maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Additionally, consider the following tips to maximize asthma prevention:
- Identify and avoid asthma triggers
- Follow the asthma management plan provided by your doctor
- Take appropriate treatment steps by recognizing the causes of asthma attacks
- Use asthma medications prescribed by your doctor regularly
- Monitor airway conditions
It is important to note that using an inhaler can increase asthma reactions. Therefore, it is essential to discuss this with your doctor to ensure that the asthma management plan is tailored to your needs. Flu and pneumonia vaccinations are also highly recommended to prevent the worsening of asthma.
If you have any health complaints, consult your doctor immediately. Remember to check your health regularly to help detect problems in your body before symptoms appear. Additionally, consider implementing ways to keep your respiratory system healthy, such as avoiding smoking, staying hydrated, and engaging in regular exercise.