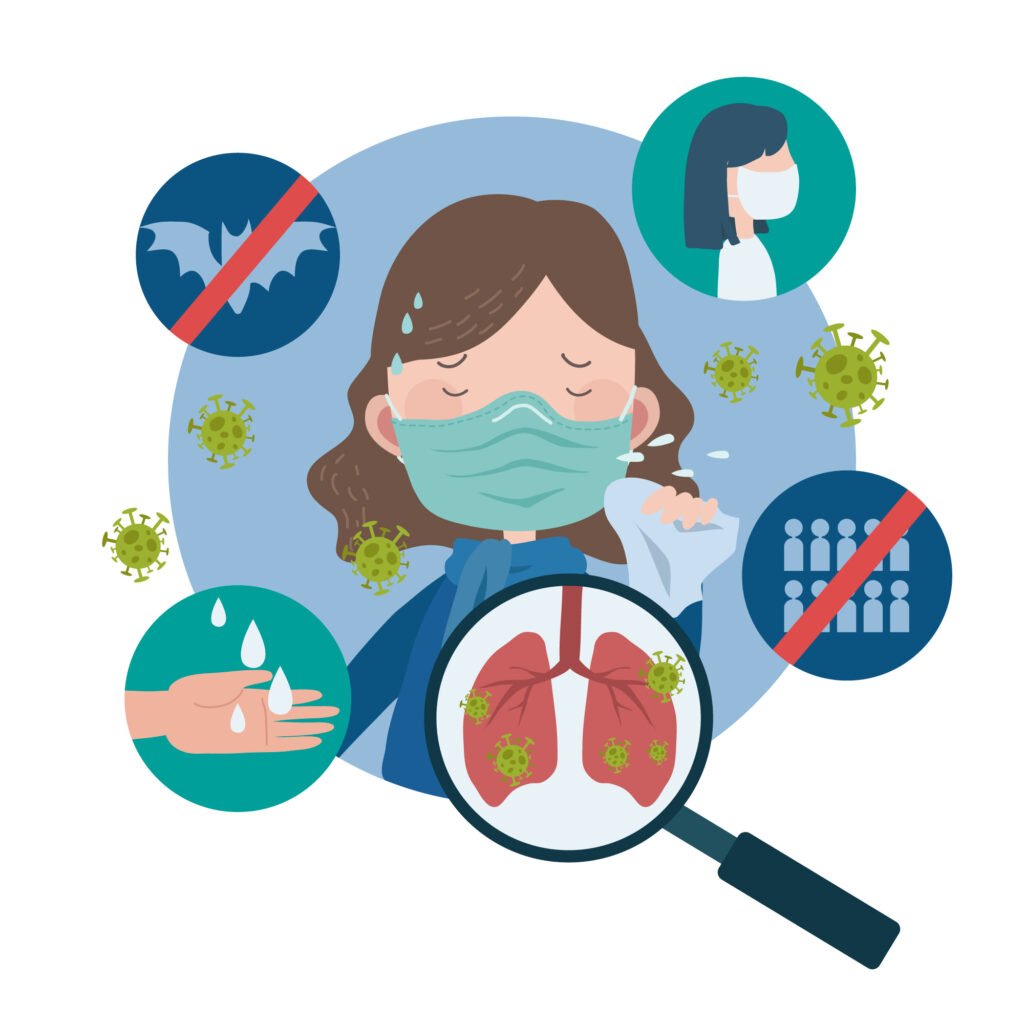
Respiratory System Diseases – The human respiratory system plays a crucial role in providing the body with the oxygen it needs. Oxygen is essential for burning energy, forming the immune system, and maintaining the body’s pH balance. H
owever, the respiratory system can also experience disruptions, leading to disturbed and suboptimal breathing processes.
Diseases of the respiratory system can affect daily activities. Without an adequate oxygen supply, the body cannot function optimally and is more susceptible to fatigue.
What Causes Respiratory System Diseases?
Several factors can cause diseases of the respiratory system, such as:
- Air cleanliness
- Allergic reactions
- Bacterial, viral, and fungal infections
- Genetic factors
- What Are the Symptoms of Respiratory System Diseases?
- When experiencing respiratory tract illnesses, several symptoms typically arise.
However, theperceived symptoms may vary from person to person depending on the type and cause of the disease. Some common symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing, either productive or dry
- Sneezing
- Fever
- Making noises while breathing (wheezing)
- Easily feeling tired
- Chest pain
What Are the Types of Respiratory Diseases?
Here are some of the most common respiratory diseases found in society:
1. Asthma
Who isn’t familiar with asthma? This respiratory tract disease is the most commonly found respiratory disorder among the population.
Asthma can cause symptoms such as difficulty breathing or shortness of breath due to narrowing of the airways in the respiratory tract.
2. Bronchitis
Bronchitis is a respiratory disorder that occurs in the bronchial tubes or branches of the airways connecting the throat and lungs.
This condition can cause productive coughing followed by shortness of breath, sore throat, and fever.
3. Pneumonia
Pneumonia, also known as lung inflammation or wet lungs, is an inflammation that occurs inside the lungs, specifically in the air sacs (alveoli).
This inflammation causes the alveoli to fill with fluid, resulting in symptoms such as coughing, both productive and dry, shortness of breath, chest pain, and fever.
4. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or COPD is a lung disease caused by narrowing of the airways, disrupting airflow, due to prolonged exposure to harmful substances in the airways.
This condition can also lead to several complications that may result in other respiratory diseases such as bronchitis and pneumonia.
The main symptoms are shortness of breath, easy fatigue, and this condition can worsen every year.
5. Pulmonary Tuberculosis (TB)
Pulmonary tuberculosis or TB is a respiratory system disease caused by infection with the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
This disease can affect many people and is transmitted through droplets from coughing or sneezing.
If left untreated, this disease can cause symptoms such as fever, coughing up blood, and shortness of breath.
6. Pulmonary Fibrosis
Pulmonary fibrosis is a condition where the lung tissue undergoes permanent damage due to progressive scar tissue from lung infections or injuries due to other factors.
This condition can impair lung function, leading to symptoms such as shortness of breath and easy fatigue.
7. Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is quite common in cases of cancer diseases both in Indonesia and worldwide.
Lung cancer can cause shortness of breath, chest pain, coughing, and weakness, and if not treated promptly, it can lead to death.
8. Asphyxia
Asphyxia refers to a condition where there is a deficiency of oxygen supply to the body’s tissues due to respiratory system problems.
This can occur in various situations such as drowning, pneumonia, or poisoning. In drowning, the airway is obstructed, preventing oxygen from reaching the lungs. Pneumonia, on the other hand, leads to inflammation and fluid buildup in the lungs, impairing oxygen exchange.
Poisoning can interfere with the body’s ability to utilize oxygen effectively at the cellular level, leading to tissue hypoxia.
Asphyxia can result in serious complications if not promptly addressed, including organ damage and even death.
9. Acidosis
Acidosis is a respiratory system disorder characterized by an imbalance in the body’s acid-base equilibrium, leading to increased levels of carbonic acid and bicarbonate acid in the blood.
This condition can occur when the lungs are unable to expel enough carbon dioxide, causing it to accumulate in the bloodstream and lower the blood pH.
Acidosis can have various causes, including respiratory diseases like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), lung infections, or metabolic disorders. Symptoms may include rapid breathing, confusion, and fatigue, and severe cases can lead to organ failure.
10. Adenoid Face
Adenoid face refers to a narrowing of the airways due to the swelling of lymph glands, often located in the throat or tonsils.
Adenoids are part of the body’s immune system and can become enlarged or inflamed, especially in children.
When swollen, adenoids can obstruct the airway, leading to symptoms such as nasal congestion, difficulty breathing through the nose, and snoring. In severe cases, adenoid enlargement may contribute to sleep apnea or recurrent ear infections.
Treatment may involve medications to reduce inflammation or surgical removal in persistent cases.
11. Diphtheria
Diphtheria is a bacterial infection caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae, which primarily affects the respiratory tract.
The bacteria produce toxins that lead to the formation of a thick, grayish membrane in the throat and nasal passages, causing obstruction of the airway. Diphtheria can result in symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, fever, and a barking cough.
Without prompt treatment, it can lead to serious complications like respiratory failure, myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle), and nerve damage.
Vaccination is essential for prevention, and treatment involves antibiotics and antitoxin therapy.
12. Emphysema
Emphysema is a chronic respiratory disorder characterized by irreversible damage to the alveoli, the small air sacs in the lungs where oxygen exchange occurs.
This damage leads to the loss of elasticity and collapse of the airways, making it difficult to exhale air properly. Emphysema is commonly associated with long-term exposure to cigarette smoke or environmental pollutants, although genetic factors may also play a role.
Symptoms include shortness of breath, chronic cough, wheezing, and chest tightness. Treatment focuses on symptom management, smoking cessation, and pulmonary rehabilitation to improve lung function.
13. Tuberculosis (TB)
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which primarily affects the lungs but can also involve other organs. TB spreads through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes, making it highly contagious.
Symptoms of TB may include coughing up blood, chest pain, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Without treatment, TB can be fatal, but it can usually be cured with a course of antibiotics taken over several months.
Prevention strategies include vaccination, early detection, and treatment of active cases, and infection control measures.
14. Inflammation of the Respiratory System
Inflammation of the respiratory system encompasses a range of conditions affecting various parts of the respiratory tract. Bronchitis involves inflammation of the bronchial tubes, leading to coughing and mucus production.
Laryngitis affects the larynx, causing hoarseness and difficulty speaking. Pharyngitis affects the throat, causing sore throat and difficulty swallowing.
Pleuritis involves inflammation of the pleura, the membranes surrounding the lungs, resulting in chest pain exacerbated by breathing. Rhinitis affects the nasal cavity, causing nasal congestion, sneezing, and runny nose.
Sinusitis involves inflammation of the sinuses, leading to facial pain, nasal congestion, and headache. Treatment varies depending on the specific condition and may include rest, fluids, pain relievers, and antibiotics for bacterial infections.
Are Respiratory System Diseases Dangerous?
Some respiratory diseases can usually be treated with medication and rest, but respiratory tract diseases can also cause serious health problems if not properly addressed. If the condition becomes serious, respiratory diseases must be promptly treated with medical intervention.
Respiratory tract diseases can affect anyone, but children are known to be more vulnerable to these infections, especially if they have habits of sucking fingers or foreign objects that can increase their risk of infection with bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
Read More Ways to Keep Your Respiratory System Healthy
How to Treat Respiratory Tract Diseases?
Respiratory tract diseases usually heal within 1-2 weeks, but there are several things you can do to speed up recovery, such as:
- Drink plenty of water
- Maintain room cleanliness
- Get plenty of rest
- Avoid sweet, spicy, dairy products, and fast food
- Avoid exposure to cigarette smoke and air pollution
When Should You See a Doctor?
If the symptoms you are experiencing do not go away or worsen, see a doctor immediately for further examination. You can visit Eka Hospital and meet with respiratory and lung specialists for direct treatment.